Frequently Asked Questions
Curious about Google's sustainability initiatives in data storage? This FAQ provides answers to common questions about Texas A&M's Google Storage Sustainability Project.

About The Project
No, all plans were made to minimize disruption in teaching, learning or research and to minimize the need for campus members to move any data from Google. There is no need to move files or purchase additional storage.
Google announced significant changes to its Google Workspace for Education service and now offers a base amount of storage for a fixed fee with the option of purchasing additional storage as needed. To adapt to this change, we must introduce new policies and processes that optimize our storage solutions to benefit the Texas A&M community. This includes storage limits plus updated policies for managing Shared Drives.
The Google Storage Sustainability Project team has gathered real-time data related to current campus usage to create a forecast of the anticipated storage space needed for our growing institution. This, coupled with input from university leadership, campus advisory groups and other stakeholders, helped create a phased approach as we transition to a paid service model.
Quotas have been put in place for My Drive and Shared Drive Accounts based on current size with a buffer to accommodate additional growth. All plans were made to avoid any disruption in teaching, learning or research and to minimize the need for campus members to move any data from Google.
Any files stored in your Texas A&M Google Workspace account that are institutional, and not personal, should remain in a storage platform offered by the university. Storing professional content in your personal account(s) or keeping it on personal hardware, such as an external hard drive, may put university data at risk.
It is everyone's responsibility to actively reduce digital clutter and practice responsible data storage. Technology Services created how-to guides that cover the following topics:
If you have a question or need support, please contact Help Desk Central.
Understanding Storage Limits
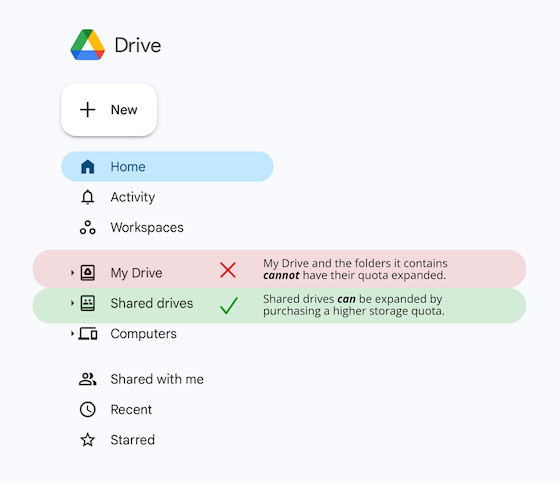
New My Drive accounts: Quotas are not expandable.
- Undergraduate students and staff receive 25 GB of storage.
- Graduate students and faculty receive 100 GB of storage.
Existing My Drive accounts:
- Undergraduate students and staff receive a 25 GB quota.
If the usage is higher, they have been alotted a quota based on their current use plus a buffer to accommodate additional growth. - Graduate students and faculty receive a 100 GB quota.
If the usage is higher, they have been alotted a quota based on their current use plus a buffer to accommodate additional growth.
New Shared Drive quotas will be 25 GB.
Existing Shared Drives will be given a 25 GB quota plus a buffer based on current usage.
Purchasing Additional Shared Drive Storage
University units may expand the quota of an existing Google Shared Drive by purchasing a higher storage quota. Quotas are available in several tiers for a one-year term:
- 1 TB Quota Tier - $150
- 2 TB Quota Tier - $300
- 5 TB Quota Tier - $750
- 10 TB Quota Tier - $1500
Units can renew, update or cancel their purchase each year.
To request additional storage, email helpdesk@tamu.edu include:
- Your storage tier
- The name of the Shared Drive
- A link to the Drive
- NetID of a manager of the Drive
Texas A&M Google Drive storage limits went into effect May, 18 2024.
Item cap
Google Shared Drives can contain a maximum of 400,000 items, including files, folders, and shortcuts. Note: This limit is based on item count, not storage use. We recommend that you keep shared drives well below the strict limit. Shared drives with too many files might be difficult to organize and search, or members ignore much of the content.
File sharing limits
A file in a shared drive can be directly shared with a maximum of 100 groups.
Folder nesting and moving
A folder in a shared drive can have up to 20 levels of nested folders. We recommend that you avoid creating many folders in one shared drive. Members might have difficulty organizing and finding content. Instead, organize content into multiple shared drives.
My Drive
When a My Drive has exceeded the storage quota customers will be unable to:
- Add new files or images to Google Drive.
- Create new files in collaborative content creation apps like Google Docs, Sheets, Slides, Drawings, and Forms.
Until you reduce storage use, no other Google users can edit or copy your affected files or submit forms owned by you. - Add or backup photos and videos to Google Photos.
- Record new meetings in Google Meet.
Note: Users can still sign in to their Google Workspace account and view and download files.
Shared Drives
When a Shared Drive exceeds its storage limit, users can't add new files or edit existing files. To resolve:
- A Content manager or Manager of the shared drive can move or delete content from the shared drive.
- Customers may create 25GB Shared Drives and reorganize content as needed.
- University employees may expand the quota of an existing Google Shared Drive by purchasing a higher storage quota. Details here.
University employees may expand the quota of an existing Google Shared Drive by purchasing a higher storage quota. Details here.
Quota Expansion Notice: Quotas can only be expanded for Shared Drives. Quota expansion is not available for My Drives or folders within My Drives.
Check Your Storage Use
To check your current My Drive storage use, go to https://drive.google.com/drive/quota. You'll see your files in descending order of file size.
The following count toward file storage:
Google Drive
- Most files in Google Drive, including PDFs, images, and videos
- Files created or edited after May 2, 2022, in collaborative content apps such as Google Docs, Sheets, Slides, Drawings, Forms, and Jamboard
- Content in shared drives
- Items in your "trash" that haven't been permanently deleted
Gmail
- Messages and attachments, including items in Spam and Trash folders
Google Photos
- Original photos and videos backed up to Google Photos
- High quality and Express quality photos backed up to Google photos after June 1, 2021
The following do not count toward file storage:
- Files in "Shared with me." Shared files are counted only for the file owner's storage, not for the users the file is shared with
- Google sites
- Drive shortcuts
- Content created with My Maps
- Version history for files created in Google Docs, Sheets, and Slides, unless the you explicitly decide to keep older versions
When managing your storage, consider prioritizing items that consume the most space, such as
- large files including videos, music, software installers
- high-resolution or raw photos
- documents with embedded images
For guidance on reviewing and decluttering your Google Drive, refer to our resource on cleaning up Google Drive. Please exercise caution when deleting files or folders, especially those shared with collaborators, as it may result in data loss for others accessing the content. Items ‘Moved to Trash’ are stored in the Trash Folder for up to 30 days. After this time they become permanently deleted.
When you first delete content, it is moved to the "trash" and will be automatically and permanently deleted after 30 days. Before the 30-day window closes, you may restore your files.
To permanently delete your files in Google Drive and make space available, you must move them to “trash” and empty your bin. Items in trash count against your storage use, until permanently deleted.
Please note: items that are permanently deleted from trash are irrecoverable.
There are no plans to migrate or delete files for active members that are currently stored in your Google My Drive. It is important to note that as part of the student account lifecycle, former student accounts will be locked and prepared for deletion after the student has been absent for two years. Any University data should be stored in a Shared Drive to ensure ongoing access.
Yes, it is possible to recover files that have been deleted from your Google Workspace for Education account, but only for a limited period of time.
Google Workspace for Education accounts have a Trash and a Bin for deleted items. When you delete a file, it is first moved to the Trash. Files in the Trash remain there for 30 days before being permanently deleted and moved to the Bin.
Files in the Bin can still be recovered by a Google Workspace administrator.
Here are the steps you can take to try and recover a deleted file:
- Check your Trash first by going to drive.google.com/drive/trash. If the file was deleted from a Shared Drive, select the drive by clicking the dropdown arrow next to 'My Drive' at the top of the page.
- If the file is still there, you can right-click on it and select "Restore" to move it back to your Google Drive.
- If the file is no longer in your Trash (after 30 days), you'll need to contact Help Desk Central to request the file be recovered from the Bin for you.
- Provide as much detail as possible about the file you need recovered, such as the file name, type, when it was deleted, etc. This will help them locate it in the Bin.
It's important to act quickly if you need to recover a deleted file, as the window of opportunity is limited, especially once files leave the Trash folder.
What About Shared Drives?
No, Shared Drives are not going away. However, part of the strategy needed to adapt to Google's service changes must include policies and practices for the creation and lifecycle management of Shared Drives.
New Shared Drive accounts will be given a 25 GB quota.
Existing Shared Drives accounts will be given a quota based on current use.
Shared Drives will go through an annual verification process to remediate old or unnecessary document storage.
University units may expand the quota of an existing Google Shared Drive by purchasing a higher storage quota. Quotas are available in several tiers for a one-year term:
- 1 TB Quota Tier - $150
- 2 TB Quota Tier - $300
- 5 TB Quota Tier - $750
- 10 TB Quota Tier - $1500
Units can renew, update or cancel their purchase each year.
To request additional storage, email helpdesk@tamu.edu include:
- Your storage tier
- The name of the Shared Drive
- A link to the Drive
- NetID of a manager of the Drive
Please refer to Viewing Storage in Shared Drives.
Yes, though it is important to understand the differences between My Drive and Shared Drives. Employee accounts are locked and deleted 30 days after the employee leaves the university. As part of the student account lifecycle, former student accounts will be locked and prepared for deletion after the student has been absent for two years. Any university data should be stored in a Shared Drive to ensure ongoing access.
Yes, Google Workspace is meant to enable teams by sharing and collaborating on documents. We are working to protect this privilege by encouraging teams to manage Shared Drives in a thoughtful and sustainable manner.
The key difference between Google Shared Drives and Google Shared Folders is ownership.
- Google Shared Drives: Ownership of the files and folders inside the drive is held by the drive itself, and all members of the drive have access to and control over the files and folders as set by the drive permissions.
- Google Shared Folders: The owner of the folder retains ownership and owner(s) of the files within the Shared Folder retain ownership.
Examples:
- Google Shared Drive: If someone leaves the university, the content created by that person in a Google Shared Drive is not affected.
- Google Shared Folder: If someone leaves the university, the content they created and shared using a Shared Folder are removed and no longer accessible by those the content was shared out to.
Enabling third-party applications within Google Workspace for Education environment carries several potential risks that must be carefully considered:
- Data privacy and security: Third-party apps may have access to sensitive student data or staff information stored in Google Workspace, posing a risk of data breaches, unauthorized access, or misuse of data.
- Compliance issues: Educational institutions are subject to various data protection regulations like FERPA and GDPR. Using third-party apps that are not compliant with these regulations can lead to violations and potential legal issues.
- Compatibility and integration issues: Third-party apps may not integrate seamlessly with Google Workspace, leading to functionality issues, data loss, or disruptions in workflow.
- Lack of control and oversight: Texas A&M University may have limited control over the security practices, data handling policies, and update schedules of third-party apps, making it difficult to ensure compliance and maintain a secure environment.
- Malware and vulnerabilities: Some third-party apps may contain vulnerabilities or malware that could compromise the security of the entire Google Workspace environment, putting sensitive data and systems at risk.
- Vendor lock-in and dependency: Relying too heavily on third-party apps can create vendor lock-in, making it difficult to switch to alternative solutions or remove the apps entirely if needed.
To mitigate these risks, Technology Services has no plan to enable third-party apps. Please contact google-project@tamu.edu, if you have any questions about third-party apps in Texas A&M Google storage.
Storage Limits For Texas A&M Gmail Accounts
Users of Texas A&M Gmail should be aware of their usage, as content stored in Gmail contributes to their My Drive storage limit. Check the total storage across Google Drive, Photos, and Gmail.
These tips can help you save space on Gmail:
- Empty your trash. Files in your trash are automatically deleted after 30 days. But while they are in trash, they count against your storage.
-
Delete messages with heavy attachments.
Attachments count towards your storage. To find emails with large attachments:
- In the search box, type “:attachment larger:10mb”.
- Click "Search."
- Check the boxes of the emails you want to delete and click the trash icon.
-
Delete very old messages.
To find older emails:
- In the search box, type “older_than:3y” (again, you can enter any number of years).
- Click "Search."
- Check the boxes of the emails you want to delete and click the trash icon.
-
Delete Spam:
- Go to your Spam folder
- Select all the messages, and delete them.
